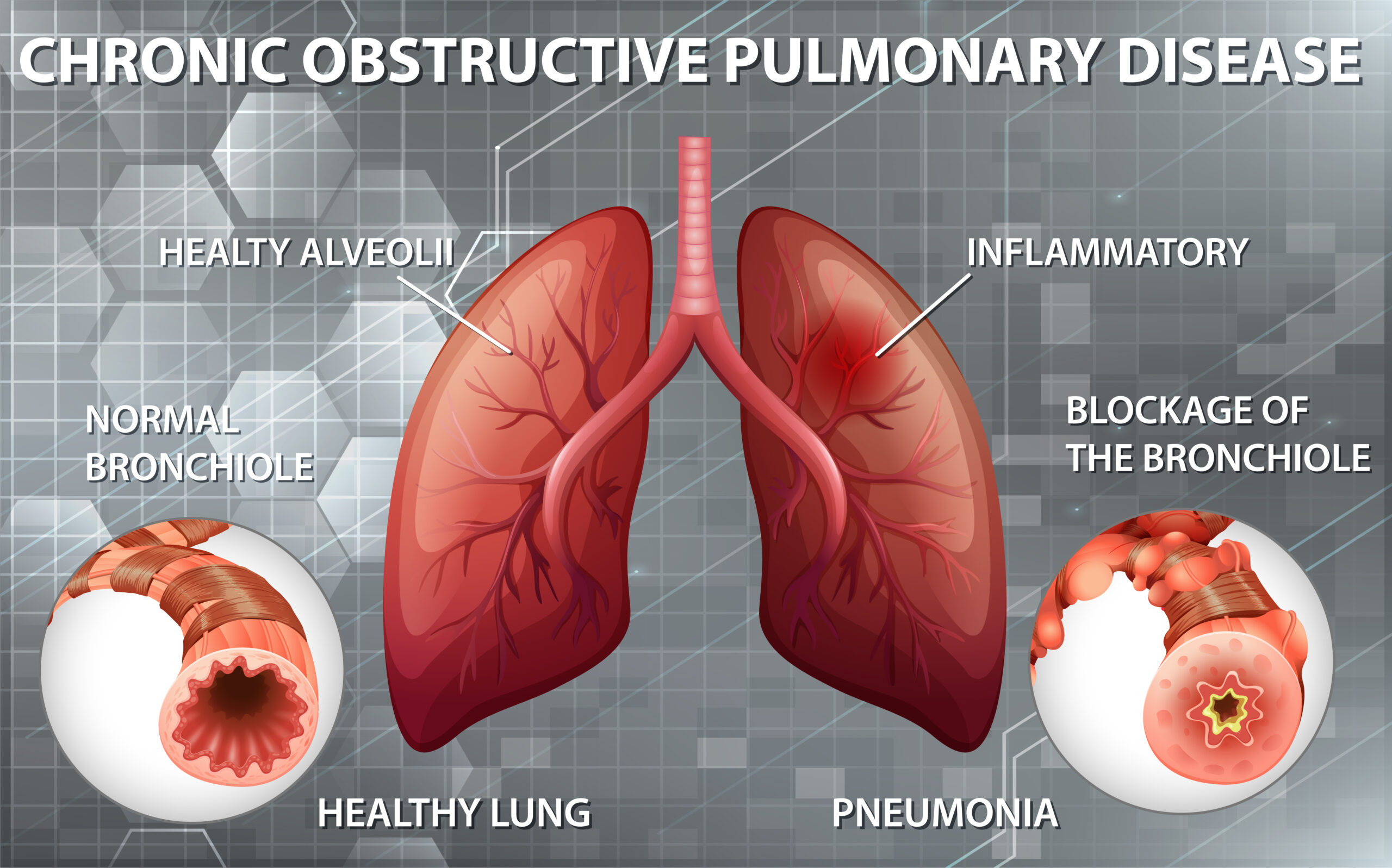
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive and debilitating respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by obstructed airflow from the lungs, COPD encompasses several respiratory illnesses, primarily chronic bronchitis and emphysema. This blog will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management strategies for COPD, providing a comprehensive overview of this serious health condition.
Causes and Risk Factors
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease develops due to long-term exposure to irritating gases or particulate matter, most often from cigarette smoke. However, other significant factors contribute to its onset:
- Smoking: The leading cause of COPD is cigarette smoking. Pipe, cigar, and other types of tobacco smoke also contribute to COPD.
- Environmental Exposure: Long-term exposure to air pollutants, chemical fumes, and dust can increase the risk of developing COPD.
- Genetics: A rare genetic disorder known as Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency can cause COPD, even in non-smokers.
- Respiratory Infections: Severe childhood respiratory infections can impact lung development and increase susceptibility to COPD in adulthood.
Symptoms of COPD
The symptoms of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease often develop slowly and can be mistaken for normal aging or other respiratory conditions. Key symptoms include:
- Chronic Cough: Often the first symptom, a persistent cough that produces mucus can be a warning sign.
- Shortness of Breath: Especially during physical activities, breathlessness is a hallmark of COPD.
- Wheezing: A high-pitched whistling sound when breathing can indicate narrowed airways.
- Chest Tightness: Discomfort or pain in the chest is a common symptom.
- Frequent Respiratory Infections: Recurring colds or infections are frequent in COPD patients.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness due to decreased oxygen levels can affect daily activities.
Diagnosis of COPD
Early diagnosis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease is crucial for managing symptoms and slowing disease progression. Several diagnostic tools are used:
- Spirometry: This lung function test measures the amount of air a person can exhale and how quickly. It is the gold standard for diagnosing COPD.
- Chest X-Ray: Can reveal emphysema, one of the main causes of COPD, and rule out other lung problems.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the lungs, helping to detect emphysema and determine the severity of COPD.
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis: Measures the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood to assess lung function.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for COPD, treatments can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life. The primary goals are to relieve symptoms, slow disease progression, prevent and treat complications, and improve overall health. Treatment options include:
Medications
- Bronchodilators: These drugs relax the muscles around the airways, making breathing easier.
- Inhaled Steroids: Reduce airway inflammation and help prevent exacerbations.
- Combination Inhalers: Contain both bronchodilators and steroids.
- Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors: Help decrease airway inflammation and relax the airways.
- Oxygen Therapy: For patients with severe COPD and low blood oxygen levels, supplemental oxygen can improve breathing and quality of life.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: A program that includes exercise, education, and support to help patients manage their condition and stay active.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Lifestyle changes and home remedies can play a significant role in managing COPD:
- Quit Smoking: The most crucial step for anyone with COPD. Stopping smoking can significantly slow the progression of the disease.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet can help maintain overall health and manage symptoms.
- Regular Exercise: Helps improve cardiovascular health and muscle strength, enhancing overall well-being.
- Avoid Lung Irritants: Minimize exposure to pollutants, secondhand smoke, and occupational dust or chemicals.
- Stay Vaccinated: Vaccinations for flu and pneumonia can prevent respiratory infections that could worsen COPD.
Conclusion
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease is a serious, progressive condition that significantly impacts a person’s quality of life. Early diagnosis, effective treatment, and lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms and improve outcomes. Awareness and education about COPD are crucial for prevention and early intervention. If you or a loved one experience symptoms of COPD, seek medical advice promptly to ensure the best possible management of this challenging condition.
If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms of COPD, early intervention is key. At Apex Pulmonology, our dedicated COPD Clinic offers comprehensive care tailored to each patient’s needs. Our team of expert pulmonologists utilizes the latest diagnostic tools and treatment options to manage and improve your respiratory health. Don’t wait—take control of your COPD today by scheduling a consultation with our specialists. Visit our COPD Clinic to learn more and start your journey towards better breathing and a healthier life.