Table of Contents
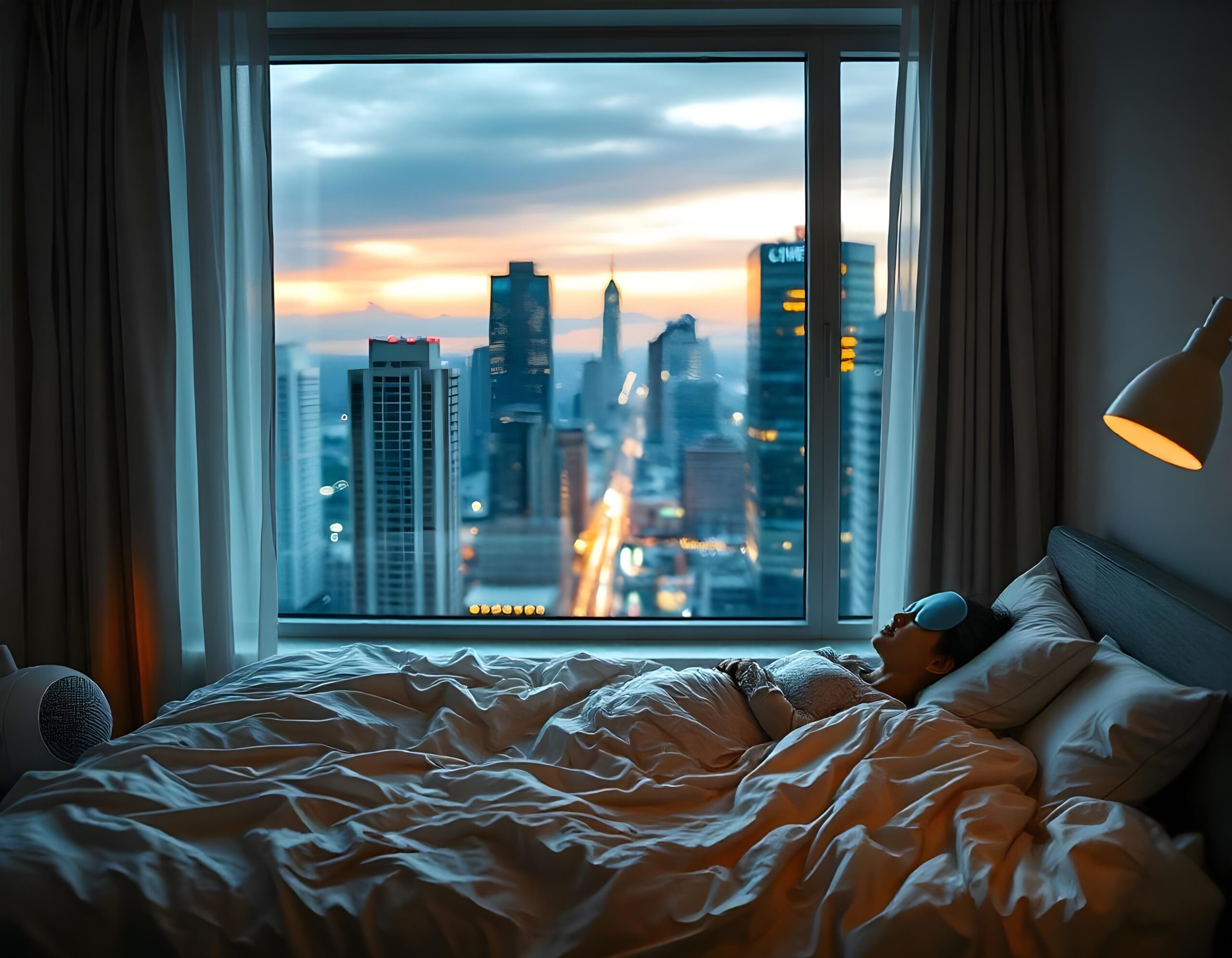
Did you know that urban dwellers often get up to 2 hours less sleep per night compared to people living in rural areas? This sleep deprivation is becoming increasingly common in the hustle and bustle of city life, where noise, light, work pressures, and lifestyle habits all contribute to poor sleep quality.
Living in the city comes with many perks: convenience, entertainment, a thriving job market, and constant social activity. However, these same benefits often come at the cost of something equally important — good, restful sleep. In this blog, we’ll explore how urban living disrupts sleep patterns and offer practical, science-backed solutions to improve your sleep quality.
Why City People Sleep Less
Urban life has a unique set of challenges that interfere with sleep. Let’s take a look at some of the most common reasons city dwellers struggle to get enough rest.
Hectic Urban Lifestyles
- Long Work Hours & Unpredictable Schedules
The fast-paced nature of city life often means longer work hours, unpredictable schedules, and a constant sense of urgency. Many people in urban areas work overtime or have irregular hours, whether due to demanding jobs or frequent travel. These long hours cut into personal time, making it hard to unwind before bed. According to studies, overwork leads to sleep deprivation and increased stress levels, both of which contribute to poorer sleep quality. - Increased Screen Time and Digital Distractions
Screens are a significant part of our lives, and in the city, they often extend well into the night. Blue light emitted by smartphones, computers, and televisions interferes with the production of melatonin, the hormone that regulates sleep. This delay in melatonin production can make it harder to fall asleep, disrupting the natural sleep-wake cycle. The temptation to scroll through social media, watch TV shows, or answer work emails at night often pushes bedtime later, affecting sleep quality.
Environmental Disturbances
- Noise Pollution
Urban environments are notoriously noisy. Whether it’s the sound of traffic, construction, or the nightlife in your neighborhood, these sounds can significantly disrupt your sleep. Research indicates that noise pollution can lead to fragmented sleep, increased cortisol (the stress hormone), and an elevated heart rate, all of which make it harder to rest. Chronic exposure to noise can also increase the risk of heart disease and high blood pressure. - Light Pollution
The bright lights from street lamps, buildings, and advertisements keep cities illuminated 24/7. Light pollution interferes with your body’s circadian rhythm, causing your body to have trouble distinguishing day from night. The result? Difficulty falling asleep and waking up at the right times. Even small amounts of artificial light can suppress melatonin production, making it harder to get a good night’s sleep.
Social Pressures and Culture
- The “Always-On” Mindset
The city culture often promotes an “always-on” mentality, where work, socializing, and entertainment take precedence over rest. Hustle culture emphasizes productivity at all hours, and this can make it difficult to switch off mentally and physically when it’s time to sleep. People tend to stretch their days into the late hours, leading to late bedtimes and insufficient sleep. - Late-Night Socializing and Entertainment
Urban areas are filled with events, nightlife, and social gatherings that can extend into the early morning hours. Late dinners, parties, and other forms of entertainment can disrupt regular sleep schedules. In fact, studies show that late-night socializing is linked to delayed sleep onset and poor sleep quality, further contributing to fatigue.
The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Urban Populations
Sleep deprivation is not just an inconvenience — it has serious consequences on both your health and well-being. Here’s how chronic lack of sleep can impact your life.
Health Impacts
- Weakened Immunity
Consistently missing sleep weakens the immune system, leaving you more vulnerable to illnesses like the common cold, flu, and other infections. Research shows that people who sleep less than 7 hours per night are more likely to get sick when exposed to viruses. - Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases and Obesity
Studies have shown a link between poor sleep and an increased risk of developing cardiovascular conditions like high blood pressure and heart disease. Lack of sleep also disrupts metabolic processes, increasing the likelihood of weight gain and obesity. This is because sleep deprivation affects the hormones that control hunger and satiety, causing you to eat more than you should.
Mental Health Consequences
- Increased Anxiety and Depression
Sleep plays a critical role in regulating mood. Insufficient sleep can lead to irritability, anxiety, and an increased risk of depression. A study by the National Institutes of Health found that people who get less sleep are more likely to experience mood swings, irritability, and emotional instability. - Decreased Focus and Cognitive Functioning
Sleep deprivation affects your brain’s ability to focus, learn, and make decisions. This results in decreased productivity at work and poor performance in daily activities. Over time, chronic sleep deprivation can lead to long-term cognitive decline, making it harder to retain information and solve problems effectively.
Work and Lifestyle Productivity
- Burnout
The combination of long hours and poor sleep creates a vicious cycle of burnout, where individuals feel exhausted yet unable to rest properly. The lack of sleep worsens job performance, making it difficult to meet work demands and causing physical and mental exhaustion. - Strained Relationships
Sleep deprivation affects your relationships, too. Irritability, lack of energy, and mood swings can lead to conflicts at work, with friends, and at home. People who don’t get enough sleep may also find it challenging to participate in social activities or connect with others in a meaningful way.
Tips to Improve Sleep in Urban Areas
If you’re struggling to get a good night’s sleep in the city, don’t worry — there are plenty of strategies to help. Here are some practical tips:
Optimize Your Sleep Environment
- Use Blackout Curtains
Block out light pollution from streetlights and nearby buildings with high-quality blackout curtains. This will create a dark environment that signals to your body it’s time to wind down. - Use White Noise Machines or Fans
Invest in a white noise machine or a fan to mask disruptive sounds from the outside, such as traffic and construction noise. You can also use earplugs for added noise cancellation. - Control Room Temperature
The optimal temperature for sleep is between 60-67°F (15-19°C). Keeping your room cool and well-ventilated can promote deeper, more restful sleep. - Use Air Purifiers
Air quality can affect sleep. If you live in an area with high pollution, an air purifier can help ensure clean, breathable air in your bedroom.
Adopt Healthy Sleep Habits
- Maintain a Consistent Bedtime Routine
A consistent bedtime routine helps signal to your body that it’s time to sleep. Whether it’s reading a book, practicing meditation, or stretching, make your pre-bedtime routine a calming ritual. - Limit Caffeine and Heavy Meals
Avoid consuming caffeine or large meals close to bedtime, as both can interfere with sleep. Caffeine is a stimulant that keeps you awake, and heavy meals can cause indigestion that disrupts sleep. - Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity helps promote better sleep, but avoid vigorous exercise too close to bedtime, as it can make it harder to wind down.
Combat Light and Noise Pollution
- Wear Sleep Masks and Use Earplugs
Sleep masks can help block out ambient light, and earplugs can block unwanted noise. Both of these can significantly improve your sleep environment in noisy, light-polluted cities. - Advocate for Better Urban Planning
Get involved in community initiatives to advocate for quieter, darker urban spaces. Urban planning that addresses noise barriers and green spaces can help create a more sleep-friendly environment.
Relaxation Techniques
- Practice Mindfulness or Deep Breathing
Mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help you relax before bed, easing both physical tension and mental stress. - Avoid Screens Before Bed
Turn off all electronic devices at least 30 minutes before bed. The blue light emitted from screens can mess with your circadian rhythm and make it harder to fall asleep.
When to Seek Professional Help
If your sleep problems persist despite making changes to your habits, it may be time to consult a professional.
- Signs You Might Need a Sleep Specialist
If you experience persistent insomnia, excessive daytime sleepiness, snoring, or difficulty staying asleep, it’s time to seek professional help. - Overview of Sleep Studies
A sleep study can diagnose sleep disorders like sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, or narcolepsy. A professional sleep evaluation can identify underlying issues and provide the best treatment plan for improving your sleep.
Conclusion
Prioritizing your sleep is essential for your physical, mental, and emotional well-being. While city life presents unique challenges to getting restful sleep, adopting healthy habits and optimizing your environment can make a significant difference.
At Apex Pulmonology, we understand the profound impact that sleep and respiratory health have on your overall well-being. If you’re struggling with sleep disorders, snoring, or any other respiratory conditions, our expert pulmonologists are here to help. Don’t wait for your sleep to deteriorate further — book a consultation with us today and take the first step towards better sleep and improved respiratory health. We offer comprehensive evaluations, including sleep studies and pulmonary function tests, to pinpoint the root causes of your issues and provide personalized treatment plans.